Hydrogen fuel cells provide a groundbreaking way to generate electricity. They use an electrochemical process that combines hydrogen and oxygen, producing electricity, water, and heat as byproducts. This clean energy solution is rapidly gaining popularity. The global market for hydrogen fuel cells is expected to grow from $11.43 billion in 2024 to $16.19 billion in 2025, with a remarkable annual growth rate of 41.7%. These systems achieve efficiencies exceeding 60% in combined heat and power setups, far surpassing traditional energy sources like internal combustion engines, which operate at only 25% efficiency. Understanding how hydrogen fuel cells work can help you appreciate their potential to transform energy use.
Key Takeaways
Hydrogen fuel cells make electricity in a clean way. They only create water and heat as waste.
New materials for catalysts have made fuel cells work better and last longer. This makes them more dependable.
Making green hydrogen using wind and solar energy is now cheaper and better for the planet.
Hydrogen fuel cells can be used in many ways. They power cars, machines, and give backup energy to important places.
Filling up hydrogen cars takes just a few minutes. This makes them a good choice for long trips instead of electric cars.
How Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work
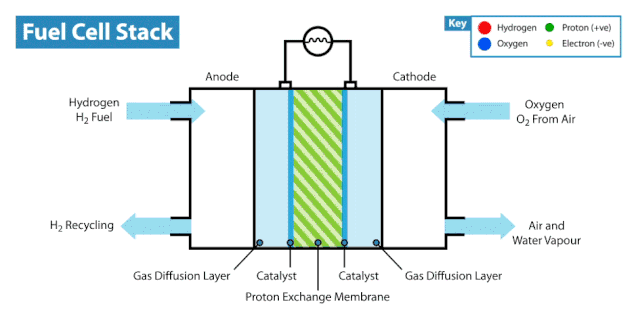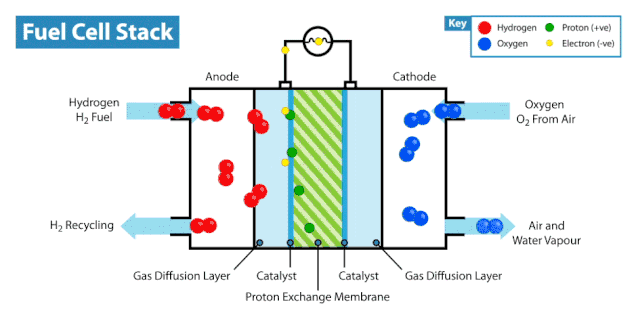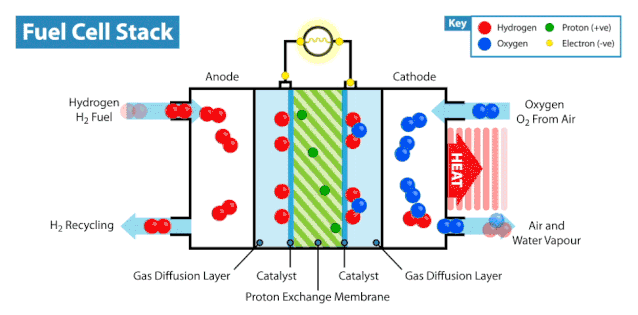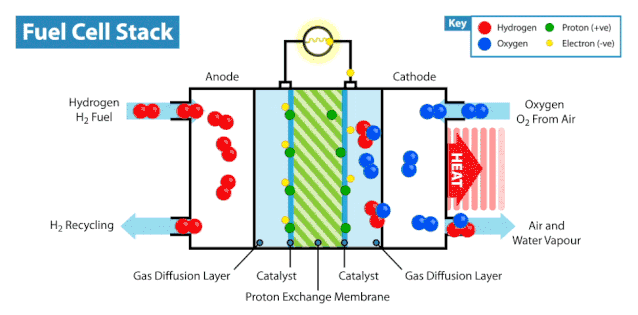
The Electrochemical Reaction
Hydrogen fuel cells rely on an electrochemical process to generate electricity. This process involves three key steps:
Anode Reaction: Hydrogen gas enters the anode, where a catalyst splits it into protons and electrons.
Proton Movement: Protons pass through the electrolyte to the cathode, while electrons travel through an external circuit, creating an electric current.
Cathode Reaction: At the cathode, protons, electrons, and oxygen combine to form water, completing the reaction.
This electrochemical process is efficient and produces only water and heat as byproducts. You can see how hydrogen fuel cells work without releasing harmful emissions, making them a clean energy solution.
Components of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Hydrogen fuel cells consist of three main components: the anode, cathode, and electrolyte membrane. Each part plays a vital role in the system. At the anode, hydrogen undergoes oxidation, splitting into protons and electrons. The electrolyte membrane allows protons to move to the cathode while blocking electrons, forcing them to travel through an external circuit. This movement generates electricity. At the cathode, oxygen reacts with protons and electrons to form water.
The coordinated function of these components ensures the system operates efficiently. Hydrogen and oxygen serve as the primary inputs, while electricity, water, and heat are the outputs. This process highlights how hydrogen fuel cells work as a sustainable energy source.
Tip: The electrolyte membrane is crucial for maintaining the separation of hydrogen and oxygen, ensuring the reaction proceeds safely and efficiently.
By understanding these components and their roles, you can appreciate the innovative design behind hydrogen fuel cells and their potential to revolutionize energy production.
Advancements in Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology
Innovations in Efficiency and Durability
New catalyst materials for better performance
You can now benefit from hydrogen fuel cell technology that uses advanced catalyst materials to improve efficiency. Recent breakthroughs include:
Platinum-group-metal-free catalysts, which have shown a 60% performance improvement compared to 2021 standards.
High-performing catalysts designed to enhance reaction rates, resulting in greater power output.
A graphene-based catalyst with platinum nanoparticles, which has demonstrated 30% less activity loss during stress tests, ensuring better durability.
These advancements make hydrogen fuel cells more reliable and cost-effective, paving the way for widespread adoption.
Extended lifespan of fuel cells
Manufacturers have introduced advanced polymers to address challenges like high temperatures and corrosive environments. These materials enhance durability and extend the lifespan of hydrogen fuel cells. For example, graphene catalysts with platinum nanoparticles have set new benchmarks for longevity, showing significant improvements in harsh conditions. This ensures that your fuel cell systems can operate efficiently for longer periods.
Green Hydrogen Production
Renewable energy-powered electrolysis
Green hydrogen is produced using renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Electrolysis splits water into hydrogen and oxygen, creating carbon-free hydrogen. Here’s a quick comparison of methods:
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Electrolysis | Splits water using renewable electricity, producing clean hydrogen. |
Scalable Photoelectrode Modules | Uses sunlight to directly split water, enhancing production efficiency. |
E-TAC Process | A membrane-free electrolysis method that improves efficiency and reduces costs. |
These methods make green hydrogen production more sustainable and competitive.
Advances in hydrogen storage and transport
Hydrogen storage and transport have seen significant improvements. Safer storage solutions, such as solid-state hydrogen storage, are now available. These advancements reduce costs and improve efficiency, making hydrogen fuel cell technology more practical for commercial applications like rail and maritime transport.
Emerging Applications
Portable and compact fuel cells
Hydrogen fuel cells are becoming more portable and compact. You can find them in vehicles that offer longer ranges and shorter refueling times compared to battery electric vehicles. They are also used in space exploration, where Alkaline Fuel Cells (AFC) power spacecraft.
High-capacity systems for industrial use
High-capacity hydrogen fuel cell systems are now powering industrial operations. Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) are used for stationary power generation and heavy machinery. In aviation, companies like Universal Hydrogen and Airbus are testing hydrogen-powered aircraft. The maritime industry has also adopted hydrogen, with the MF Hydra ferry leading the way. These applications highlight the versatility of hydrogen fuel cell technology in meeting diverse energy needs.
Applications of Hydrogen Fuel Cells

Transportation
Hydrogen-powered vehicles, including cars and buses
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (HFCEVs) are transforming mobility by offering cleaner and more efficient alternatives to traditional vehicles. These vehicles are lighter and more efficient than internal combustion engines and battery electric vehicles. For instance:
Semi-trucks powered by hydrogen fuel cells can carry up to 8,000 pounds more cargo than their electric counterparts.
Hydrogen-powered cars achieve ranges of up to 800 miles, far exceeding most electric vehicles.
Refueling takes only a few minutes, making them ideal for long-distance travel.
Hydrogen fuel cells also reduce battery maintenance costs, and advancements in technology are making these vehicles more affordable. By using domestically produced hydrogen, you can support local economies and enhance energy security.
Applications in aviation and maritime industries
Hydrogen fuel cells are revolutionizing aviation and maritime mobility. In aviation, companies like Universal Hydrogen and Airbus are testing hydrogen-powered aircraft, with commercial models expected by 2025. In the maritime sector, the MF Hydra ferry, launched in 2023, became the world’s first liquid hydrogen-powered ferry.
Industry | Project/Development | Year |
|---|---|---|
Maritime | MF Hydra – the world’s first liquid hydrogen-powered ferry | 2023 |
Aviation | Universal Hydrogen and Airbus ZEROe – developed and flight-tested hydrogen aircraft | 2025 |
These advancements highlight the versatility of hydrogen fuel cells in addressing diverse mobility needs.
Energy Sector
Grid energy storage solutions
Hydrogen fuel cells provide innovative solutions for energy storage. They balance supply and demand by storing excess energy produced during off-peak hours. Electrolyzers convert surplus power into green hydrogen, which is stored for later use. This stored hydrogen can then power fuel cells or gas turbines during peak demand. These technologies integrate seamlessly with existing energy systems, enhancing grid stability and reliability.
Backup power for critical infrastructure
Hydrogen fuel cells offer reliable backup power for critical infrastructure like hospitals, data centers, and emergency services. Their ability to provide immediate power generation ensures uninterrupted operations during outages. These systems also mitigate fluctuations in renewable energy sources, acting as both a power source and reserve energy.
Industrial Use
Powering heavy machinery and manufacturing
Hydrogen fuel cells are powering heavy industrial vehicles and machinery, reducing greenhouse gas emissions in sectors like construction and mining. Their versatility supports applications in stationary power generation and portable power solutions. This makes them a key player in industrial mobility and energy solutions.
Hydrogen as a feedstock for industrial processes
Hydrogen plays a vital role as a feedstock in industries like ammonia production, oil refining, and methanol production. For example:
Hydrogen is essential in ammonia production, which is projected to grow by 40% over the next 30 years.
It acts as a catalyst in methanol production by interacting with carbon monoxide.
Emerging applications include its use in steelmaking to reduce emissions.
Clean hydrogen is becoming increasingly important as industries strive to lower their carbon footprints.
Comparing Hydrogen Fuel Cells to Other Energy Technologies
Hydrogen Fuel Cells vs. Batteries
Efficiency and energy density
When comparing hydrogen fuel cells to batteries, you’ll notice significant differences in efficiency and energy density. Batteries boast an energy conversion efficiency of 80-90%, while hydrogen fuel cells achieve 40-60%. However, hydrogen fuel cells excel in energy density, offering 39.6 kWh/kg compared to lithium batteries’ 0.15-0.25 kWh/kg. This makes hydrogen fuel cells ideal for mobility purposes, especially in applications requiring long ranges or heavy loads.
Technology | Energy Conversion Efficiency | Energy Losses | Energy Density (kWh/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
Batteries | 80-90% reuse | Lower losses | 0.15 – 0.25 |
Hydrogen Fuel Cells | 40-60% conversion | Higher losses | 39.6 |
Refueling time vs. charging time
Hydrogen fuel cells also outperform batteries in terms of refueling time. While charging a battery can take hours, refueling a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle takes only a few minutes. This advantage makes hydrogen fuel cell fleets more practical for commercial and public transportation.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells vs. Internal Combustion Engines
Emissions and environmental impact
Hydrogen fuel cells offer zero emission power, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. In contrast, internal combustion engines emit harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases. If you use green hydrogen, the environmental benefits increase further, as the entire energy production cycle becomes nearly carbon-free.
Note: Hydrogen fuel cells can reduce CO2 emissions by 50% when hydrogen is produced from natural gas. With renewable hydrogen gas, emissions drop even more significantly.
Scalability and infrastructure needs
Scaling hydrogen fuel cells requires addressing challenges like high-pressure storage and the availability of hydrogen fueling stations. While the infrastructure for internal combustion engines is well-established, hydrogen fuel cell systems need further investment to become widely accessible. However, advancements in green hydrogen production and storage are making this technology increasingly viable.
Cost and Scalability
Current costs and challenges
The cost of hydrogen fuel cell systems has decreased significantly over the years. For example, the cost of automotive fuel cell systems dropped from $55 per kilowatt in 2014 to $40 per kilowatt by 2020. However, challenges remain, including the high costs of hydrogen production, storage, and transportation.
Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
High-Pressure Storage and Transport | Hydrogen must be stored and transported at high pressures, which is costly and requires specialized equipment. |
Cost of Hydrogen Production | The production, storage, and transportation of hydrogen are expensive compared to traditional energy sources. |
Future potential for cost reduction
Ongoing research and development are driving down costs. Innovations in electrolyzers have reduced their cost by over 90% since 2001. Improved catalysts and optimized fuel cell designs are also enhancing efficiency and lowering production costs. These advancements make green hydrogen fuel cells more competitive in the energy market.
Hydrogen fuel cells represent a clean and efficient energy solution with immense potential. They achieve efficiencies up to 60%, far surpassing traditional combustion engines. Recent advancements, such as enhanced catalysts and sophisticated membranes, have improved performance and durability. By producing hydrogen from renewable sources, you can significantly reduce emissions and support a sustainable future. These versatile systems power vehicles, industrial processes, and critical infrastructure, making them essential for meeting future energy demands. As the world transitions to greener energy, hydrogen fuel cells will play a pivotal role in reducing global emissions and ensuring energy resilience.
FAQ
What is the main advantage of hydrogen fuel cells over traditional energy sources?
Hydrogen fuel cells produce electricity with zero harmful emissions. They only emit water and heat as byproducts. This makes them a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, helping you reduce your carbon footprint.
How long does it take to refuel a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle?
Refueling a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle takes about 3-5 minutes. This is much faster than charging an electric vehicle, making it a convenient option for long-distance travel or commercial fleets.
Are hydrogen fuel cells safe to use?
Yes, hydrogen fuel cells are safe. Modern systems use advanced materials and designs to prevent leaks and ensure safe operation. Hydrogen is stored in high-pressure tanks that meet strict safety standards, giving you peace of mind.
Can hydrogen fuel cells work in cold climates?
Hydrogen fuel cells perform well in cold climates. They can operate at temperatures as low as -30°F (-34°C). This makes them suitable for a wide range of environments, including regions with harsh winters.
What are the main challenges of hydrogen fuel cell adoption?
The main challenges include high production costs, limited fueling infrastructure, and hydrogen storage issues. However, ongoing advancements in technology and government support are addressing these barriers, making hydrogen fuel cells more accessible for you in the future.


